Sexually Transmitted Infections/Diseases
When you engage in any sexual activity with another person without using a form of protection such as condoms, you are at risk of getting a sexually transmitted infection (STI).
“STD” and “STI” are often used interchangeably; STD stands for “sexually transmitted disease”, while “STI” stands for “sexually transmitted infection”. Infections develop into diseases when they cause symptoms. The three main causes of STIs are bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
If you experience any symptoms or would like to be tested for STIs, contact your healthcare provider or visit the Find a Doctor page to find a provider near you. To learn about STI testing, visit the Getting Tested page.
In addition, check out this video about STIs.
There are four ways you can get an STI, shown in the picture below.
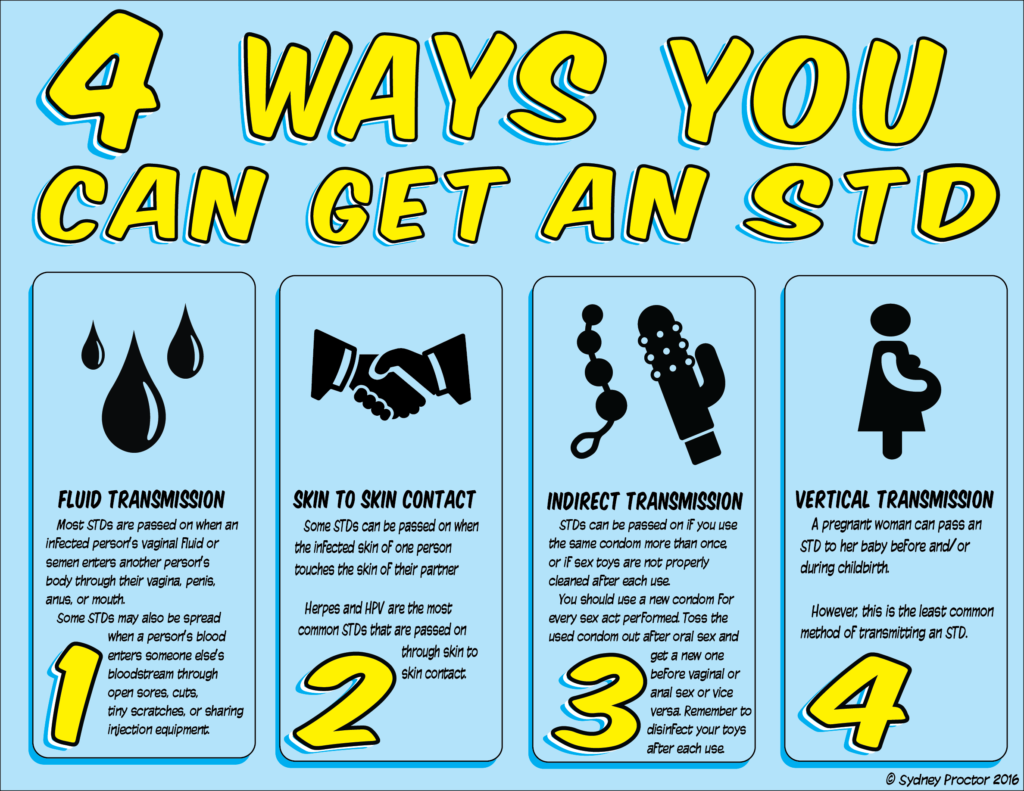
- Penile or vaginal discharge
- Burning feeling during urination
- Pelvic pain
- Fever/chills
- Genital lumps or bumps
- Itching or burning in the genitals
- Painful sex

If you experience any symptoms or would like to be tested for STIs, contact your healthcare provider or visit the Find a Doctor page to find a provider near you. To learn about STI testing, visit the Getting Tested page.
- Not being tested for STIs between sexual encounters with different partners
- Engaging in risky sexual behaviors
- Unprotected sex (not using a condom)
- Having more than one sexual partner
- Having sex with someone who has/had multiple sexual partners or injected drugs
- Having sex under the influence of drugs or alcohol
- Trading sex
- Abstinence
- Using a condom every single time you have sex
- Getting tested every time you have a new partner
- Communicating with your partners about your STI testing
Below is a list of STIs organized by their three main causes: bacteria, viruses, and parasites. You can learn more about each STI from these pages: Planned Parenthood and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
STIs Caused by Bacteria
These STIs can be treated with antibiotics.
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Syphilis
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
STIs Caused by Viruses
These STIs are incurable, but there are ways to protect against and control them.
- HIV/AIDS. HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is the virus that causes AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV). There is an HPV vaccine you can get to protect yourself against this virus, and it also helps protect you against specific cancers. The CDC provides the following recommendations regarding the HPV vaccine:
- 2 shots given over 6 months apart to people under age 15.
- The earliest you can get the HPV vaccine is 9 years old.
- If you start getting vaccinated after your 15th birthday, you will need 3 shots given over 6 months apart.
- If you haven’t been vaccinated already after age 26, you can still get vaccinated through age 45 and be covered by health insurance.
- 2 shots given over 6 months apart to people under age 15.
- Genital Herpes
- Hepatitis
STIs Caused by Parasites
These STIs can be treated with antibiotics.
- Trichomoniasis
- Pubic lice (crabs)
- Scabies
Content reviewed by Shandhini Raidoo, MD, MPH, FACOG
Last Updated: September 25, 2020 by Phyllis Raquinio